Greater Bengaluru Authority – List Of GBA Corporations, Maps, And More
Greater Bengaluru Authority or GBA (formerly BBMP) has introduced a new model of city administration for Bengaluru. GBA is formed under the Greater Bengaluru Governance Act (GBGA), 2024. The GBA is formed to improve governance, decentralization, and service delivery.
Under this Act, the existing Bruhat Bengaluru Mahanagara Palike (BBMP) is being restructured into five independent municipal corporations, each headed by its own Mayor and Commissioner, but overseen by a Greater Bengaluru Authority for coordination.
What Is Greater Bengaluru Authority (GBA)?
The Greater Bengaluru Authority (GBA) is the new governing and planning body established to streamlining administration, urban planning, and infrastructure development across the Bengaluru Metropolitan region.
GBA Highlight
- Announced in: 2024
- Established through: Greater Bengaluru Governance Bill
- Replaces BBMP as the top-level authority.
- Encompasses 5 new municipal corporations (besides the existing BBMP wards).
Objectives Of Greater Bengaluru Authority
- Decentralize governance in a city of over 1.3 crore people
- Improve civic management, infrastructure, and service delivery
- Empower local wards while ensuring unified city planning
What It Means for Bengaluru
- Unified Governance: Instead of only BBMP handling core city issues, GBA will oversee the entire metropolitan region, ensuring coordination among multiple corporations and planning bodies.
- Metropolitan Scale Planning: Covers city limits + surrounding areas that function as Bengaluru’s economic and residential extensions.
- Better Infrastructure Management: Focus on transport, waste management, water supply, and urban amenities.
- Decentralisation: Power and funds expected to be devolved at ward and zonal levels for efficient local governance.
Key Difference Between GBA And BBMP
Greater Bengaluru Authority – List Of 5 Corporations And Assembly Constituencies
| Municipal Corporation | Assembly Constituencies | Areas Covered | Headquarters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bengaluru Central City Corporation (BCC) | Chickpet Gandhi Nagar Shanti Nagar Pulakeshi Nagar Chamarajpet Shivaji Nagar | MG Road, Vidhana Soudha, Shivajinagar, Rajajinagar, Basavanagudi, Jayanagar, Gandhinagar | Hudson Circle |
| Bengaluru South City Corporation (BSCC) | BTM Layout Bangalore South Bommanahalli Jayanagar Padmanabhanagar Mahadevapura (Bellandur part) | JP Nagar, Banashankari, BTM Layout, Kumaraswamy Layout, Uttarahalli | Jayanagara |
| Bengaluru East City Corporation (BECC) | KR Puram Mahadevapura (excluding Bellandur) | Whitefield, Mahadevapura, KR Puram, Indiranagar, CV Raman Nagar | Mahadevapura |
| Bengaluru West City Corporation (BWCC) | Malleswaram Basavanagudi | Basavanagudi: Bull Temple area; Malleswaram (ward names TBD) | Rajarajeshwarinagara |
| Bengaluru North City Corporation (BNCC) | Byatarayanapura Dasarahalli Hebbal Pulakeshi Nagar Rajarajeshwari Nagar Sarvagna Nagar Yelahanka | Vijayanagar, Nagarabhavi, Kengeri, Chandra Layout, Magadi Road area | Yelahanka |
Greater Bengaluru Authority – Area, Population, And More
| Corporation | Area (sq km) | Population (2023, in millions) | Density (per sq km) | Projected Property Tax Collection (2025, ₹ Cr) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central | 78 | 1.23 | 15,769 | 659 |
| East | 163 | 3.15 | 19,328 | 992 |
| North | 158 | 1.53 | 9,620 | 553 |
| West | 161 | 4.45 | 27,637 | 1,077 |
| South | 152 | 1.47 | 9,671 | 537 |
| Total | 712 | 11.44 | 22,807 (avg) | 3,767 |
Greater Bangalore Map (GBA Map)
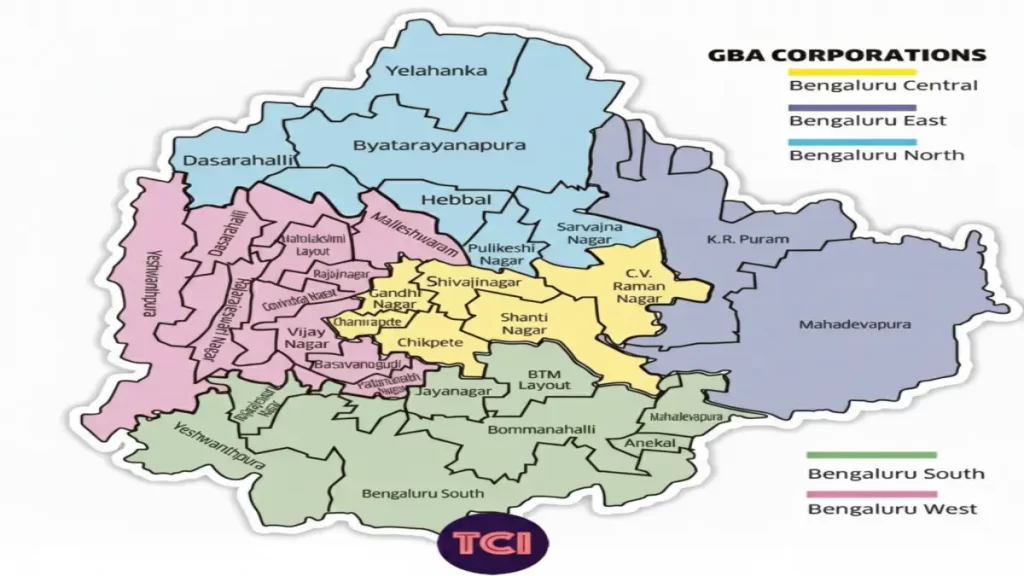
The Greater Bengaluru Governance Act, 2024
The Greater Bengaluru Governance Act, 2024 (Karnataka Act No. 36 of 2025) is a law passed by the Karnataka legislature to redefine and reorganize the governance and administration of Bengaluru and its metropolitan region.
Its purpose is to introduce a framework of institutions, processes, and powers for effective urban governance in what is called the Greater Bengaluru Are.
The ACT replaces and supersedes prior laws (notably the BBMP Act, 2020) governing Bengaluru’s municipal administration.
The Need For The Greater Bengaluru Governance Act, 2024
- Bengaluru’s growth over decades created a highly fragmented institutional setup: multiple civic agencies (water, transport, development authorities) operating with overlapping roles and poor coordination.
- The existing system under BBMP and associated Acts was not structured to handle metropolitan-scale issues, large infrastructure projects, or uniform planning across expanding suburbs.
- The new Act aims to integrate planning, streamline functions, and strengthen accountability and citizen participation across the larger urban region.
Key Features Of The Greater Bengaluru Governance Act, 2024
Three-tier Governance Model
- Greater Bengaluru Authority (GBA) — a metropolitan apex body
- City Corporations — up to seven independent local bodies under the GBA
- Ward Committees — grassroots level participatory units
Dissolution & Vesting of BBMP and other local bodies
When the Act comes into force, BBMP and other existing municipal/ local bodies within the defined area are dissolved, and their assets/liabilities vest in the State (until reassigned) or in the new entities.
Constitution of GBA
- The Chief Minister acts as ex-officio Chairperson.
- A Chief Commissioner (senior government official) is appointed as the principal executive head.
- Members include ministers, MLAs, MPs whose constituencies fall within Greater Bengaluru, and mayors of the city corporations.
Powers and functions
- GBA is tasked with coordinating and supervising public authorities (water, transport, electricity, etc.) in the area, issuing binding directions.
- Acts as the planning authority for the Greater Bengaluru Area under the Karnataka Town & Country Planning Act.
- It can plan and execute major infrastructure projects that span across city corporation boundaries.
- GBA must establish an Economic Development Agency and a Climate Action Cell to guide growth and sustainability.
Financial and accountability measures
- GBA can receive grants, borrow funds, and prepare its own budget.
- Its accounts are subject to audit (including oversight by Comptroller & Auditor General) and an annual reporting requirement.
Territorial flexibility
- The State Government can notify and revise the boundaries of the Greater Bengaluru Area over time.
The Greater Bengaluru Governance Act – Implementation And Transition
- The law came into effect starting May 15, 2025, as the “appointed date” for restructuring to begin.
- During the transition, BBMP continued to function until GBA and the new corporations became fully operational (by September 2, 2025).
- The law allows up to seven city corporations to be formed within its jurisdiction; the government started with five initially.
The Greater Bengaluru Governance Act 2024 PDF

Greater Bengaluru Authority – Top FAQs
Which areas come under Greater Bangalore?
Greater Bangalore includes Core city + CMCs + TMC + Villages, covering an area of about 741 sq km and divided into 198 wards:
City Municipal Councils (CMCs) under GBA
1. Rajarajeshwari Nagar
2. Dasarahalli
3. Bommanahalli
4. Krishnarajapura (KR Puram)
5. Mahadevapura
6. Byatarayanapura (Yelahanka region)
7. Kengeri
Town Municipal Council (TMC):
1. Yelahanka
What are the 5 corporations in Bangalore?
The 5 new corporation in Bangalore are Central Corporation, East Corporation, West Corporation, North Corporation and South Corporation.
Is Bengaluru no longer under BBMP?
No. Bruhat Bengaluru Mahanagara Palike (BBMP) was officially dissolved on, paving the way for Greater Bengaluru Authority
Does electronic city come under Greater Bengaluru Authority?
Yes. In addition to Electronic City, The Greater Bengaluru Authority also include areas such as Sarjapur, Attibele, Bommasandra, Jigani, Bagalur,, Hesaraghatta, Rajanakunte, Dasanapura, Tavarekere, Makali, Kumbalagodu, Harohalli, and Kaggalipura, .
What is Greater Bengaluru Area?
The greater Bengaluru area refers to the larger metropolitan region surrounding Bengaluru city that goes beyond the core limits of Bruhat Bengaluru Mahanagara Palike (BBMP).
The greater Bengaluru area includes:
1. Bengaluru Urban district
2. Parts of Bengaluru Rural district
3. Parts of Ramanagara district
The idea of greater Bengaluru area is similar to other global metropolitan regions (like Greater London or Greater Tokyo). It captures the economic, residential, and industrial zones that are interconnected with Bengaluru city.
You May Like